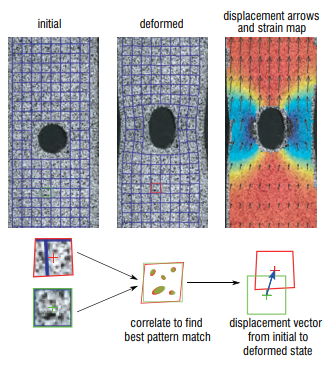
Digital Image Correlation (DIC)
Digital Image Correlation (DIC) effectively tracks the movement of the naturally occurring, or applied surface pattern during the test or experiment. This is done by analyzing the displacement of the patterns within discrete subsets or facet elements of the whole image. The maximum correlation in each window corresponds to the displacement, and this gives the vector length and direction for each window.
Continue Reading: digital-image-correlation-dic.html
TECHNIQUE: 2D-/3D STEREO DIGITAL IMAGE CORRELATIOn
|
Digital Image Correlation (DIC) tracks the movement of the naturally occurring or applied surface pattern during the test or experiment. This is done by analyzing the displacement of the pattern within subsets of the whole image using a technique called Least Square Matching.
Least Square Matching is a method for the geometric and radiometric matching of two or more image patches from a reference image (template) with respect to a search image. calibrationThe purpose of the calibration is to find the intrinsic and extrinsic parameters of a camera model that best describes the optical system. Intrinsic parameters are mainly characteristics of the lens, like focal length or radial and tangential distortions, while extrinsic parameters define the standoff distance from the object and general camera pose in space.
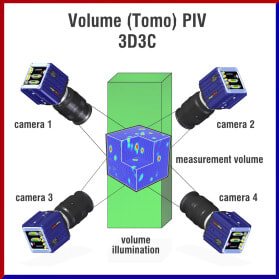
The simplest calibration for a 2D system would be a pix/mm scaling, however this would not account for optical distortions. Without calibration, the strong compressive distortions around the edges of the raw image would introduce artificial strains in DIC when moving a pattern from the center of the image towards the border. In 3D stereoscopic DIC systems, two cameras view the surface of the specimen. The camera system is calibrated such that the relationship between raw and world space is known. By matching the pattern between cameras and using the calibration model, the height and z-displacement of the surface can be calculated. |
Related Instruments
|
*Pictures shown above are for reference only. Actual product may differ slightly.
**Some products may not be available in all countries. Please contact us for further information and clarification. |
Don't have what you are looking for?
Search Here. Alternatively, please contact us for more information.
|